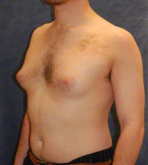
 Enlarged male breast tissue can be caused by many factors ranging from endocrine abnormalities to normal adolescence. In some cases, blood tests to check levels of sex and thyroid hormones are necessary. If one side has a mass that is tender and growing, a biopsy to rule out cancerous changes may be necessary. But the most common cause after puberty is benign hypertrophy not related to a pathologic condition. Most benign hypertrophy (enlargement) is caused by excess fat deposits on the chest, but sometimes there are actual breast glands that add to the increased size. Benign enlargement of the breast can be corrected with surgery.
Enlarged male breast tissue can be caused by many factors ranging from endocrine abnormalities to normal adolescence. In some cases, blood tests to check levels of sex and thyroid hormones are necessary. If one side has a mass that is tender and growing, a biopsy to rule out cancerous changes may be necessary. But the most common cause after puberty is benign hypertrophy not related to a pathologic condition. Most benign hypertrophy (enlargement) is caused by excess fat deposits on the chest, but sometimes there are actual breast glands that add to the increased size. Benign enlargement of the breast can be corrected with surgery.
What type of surgery is best for the male breast depends on the severity of enlargement and the presence of actual breast tissue. In mild forms, simple liposuction is all that is necessary. If there is a modest amount of excess skin, a “donut” or ring of skin is removed around the areola in addition to liposuction removal of excess volume. If actual breast tissue is responsible for the appearance, this tissue is usually removed with direct surgical excision through an incision around the areola. In some cases ultrasonic liposuction can be used instead of direct excision.
Whichever method is chosen to improve the appearance of gynecomastia, the post-operative course usually involves a garment. The purpose of the garment is to avoid fluid collections, and decrease swelling. Most patients find this compression vest comfortable and easy to wear for the required two to three weeks. There is usually little discomfort and no significant impact of work schedule.


